According to the report of an expert in the field of international financial law Konstantin Krypopustpresented by the Ministry of Statistics last month White book on the regulation of AI in Ukraine. This document describes the approach to the implementation of the future regulation of artificial intelligence in Ukraine and the steps towards it. The developers of the White Book promise that it takes into account the interests of all the key stakeholders of the sphere – citizens, businesses and the state. Is it really so? FinTech Insider reviewed the document.
The Minister of Digital Transformation, Mykhailo Fedorov, emphasized that the sphere of defense remains out of regulation, taking into account the realities of war. According to him, AI products that help fight the enemy should not be limited, but implemented as much as possible. Fedorov also noted that the development of Ukraine requires maximum deregulation and reduction of bureaucracy in order to remove obstacles to the introduction of technologies.
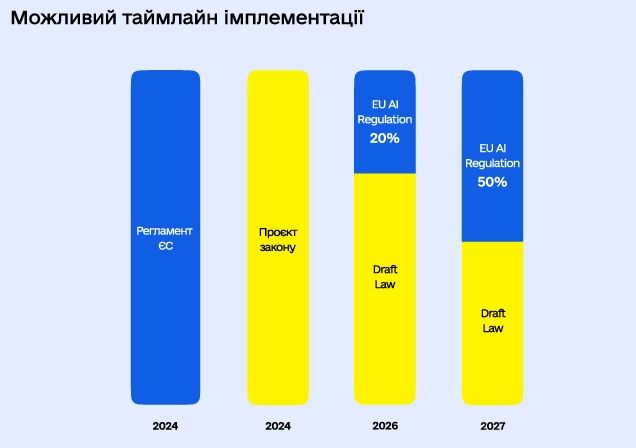
At the same time, the authors of the White Paper take into account the danger of the rapid development of artificial intelligence and its potential impact on human rights, which the whole world is currently talking about. Therefore, an approach is proposed that addresses the challenges without introducing mandatory regulation in the next 2–3 years.
The white paper provides specific tools, some of which the business can use now. They will make it possible to prepare for entering the EU market, where the relevant regulation will soon be approved. The next stage is to harmonize Ukrainian legislation with EU legislation.
Use of AI in Ukraine
Ukraine is not an exception to the global trend, and according to the January poll by Kantar Ukraine, 78.7% of surveyed citizens know what artificial intelligence is. At the same time, only 7.6% said that they do not know what AI is. Another 13.7% could not give an unambiguous answer. Also, a significant share of Ukrainian citizens already had experience using AI technologies, starting from interaction with chatbots and ending with the use of household appliances that contain artificial intelligence technologies.
According to the results of the last survey in January 2024, 29.1% of respondents indicated that they use AI in one or another field, 16.6% could not give a clear answer and 54.3% indicated that they do not use AI.


50% of respondents have a positive attitude towards AI in general, and 73% agree with the statement that AI can improve the lives of mankind. Despite the generally favorable attitude towards AI, citizens also feel the risks associated with AI — ethical, socio-economic and existential.
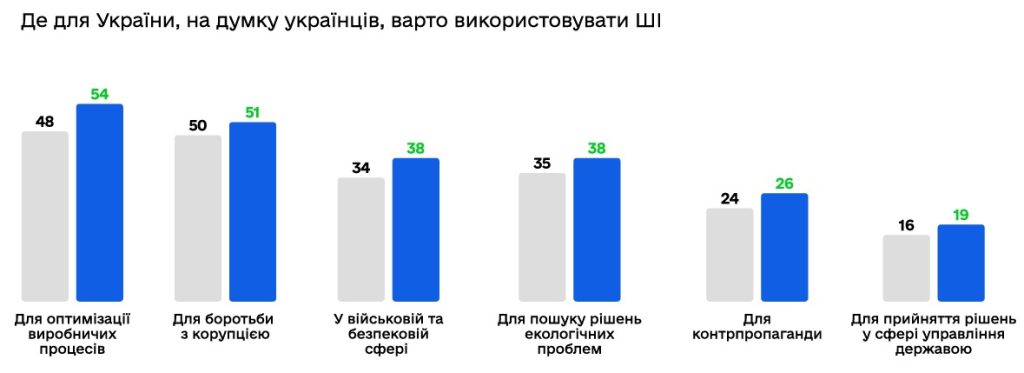
45% of Ukrainians polled by Kantar Ukraine believe that Ukraine needs a law on artificial intelligence.
Objectives of implementation of regulation
1. Support of business competitiveness.
In particular, thanks to the development and implementation of tools to prepare businesses for the introduction of regulation. It will also provide companies with access to global markets.
2. Protection of human rights.
AI has the potential not only to become another area or environment where human rights may be violated, but also to significantly increase the number of cases of human rights violations. That is why, as the Ministry of Digitization notes, in order to protect citizens from such risks and protect human rights during interaction with AI, there is a need to implement legally binding and comprehensive regulation, which is proposed at the second stage of the approach.
3. European integration.
The government is convinced that the implementation of the EU Regulation on AI is important not only for the smooth integration of Ukraine into the EU, but also has strong market and economic prerequisites. Therefore, the proposed provisions are aimed at adapting national legislation to EU legislation in this area.
Stages of regulation implementation
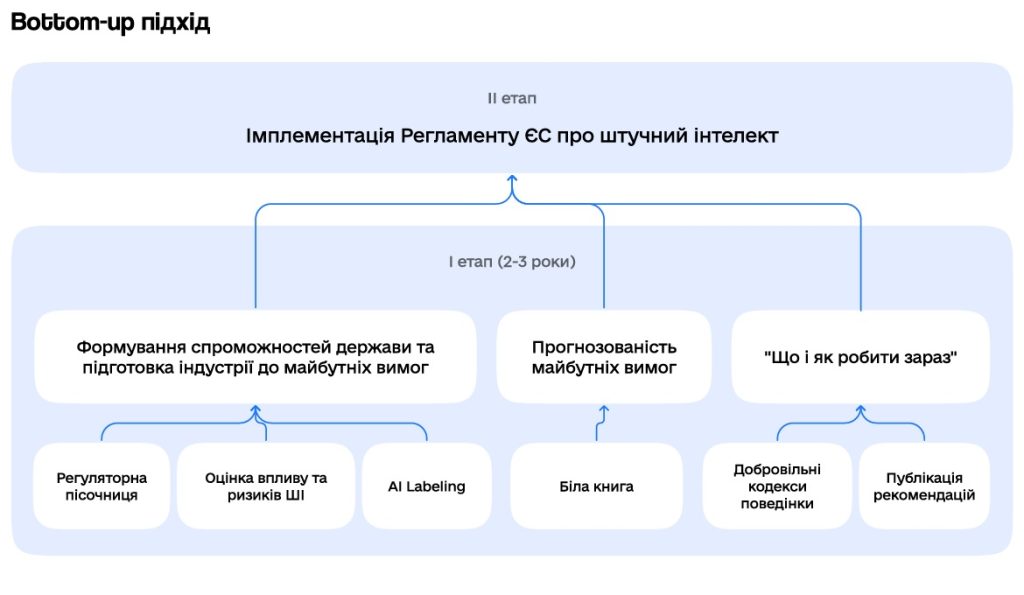
The Ministry of Digital Transformation of Ukraine proposes to use the method of gradual introduction of regulation in the field of AI, dividing it into two stages:
1. Preparatory. It envisages the creation and implementation of non-legislative tools to help specialized businesses and other stakeholders prepare for future mandatory regulation.
Currently, the development, adaptation and implementation of such tools as regulatory sandbox, AI human rights impact assessment methodology, AI labeling tools, as well as soft law tools: voluntary codes of conduct and general and sectoral recommendations are envisaged.
An important element of the first stage and the approach in general is the creation of a responsible AI web portal where such tools will be collected and integrated.
The result of the first stage should be the development and adoption of a law similar to the EU Regulation on artificial intelligence.
2. Implementation of the EU Regulation on artificial intelligence. The Ministry of Digitization notes that the EU Regulation will be one of the most effective mechanisms for the protection of human rights in the world, taking into account the final version of the regulation, the progress of the discussion on its adoption and the previous experience of implementing EU legislation in the digital sphere. And the introduction of such regulation will provide companies with access to new markets.
In April 2024, an explanatory meeting was held between Ukraine, Moldova on the one hand, and the EU on the other. During the meeting, as the Ministry of Digital Affairs notes, Ukraine received the EU’s vision and position on how candidate countries should adapt EU legislation, in particular, in the digital sphere. The EU side also emphasized the need for Ukraine to implement the EU Regulation on artificial intelligence as a virtually no-alternative path.
Regulatory sandbox of the Ministry of Statistics
In addition to artificial intelligence, the regulatory sandbox is expected to cover areas such as WEB3, blockchain and some other innovative areas. A regulatory sandbox is a controlled environment in which AI products will have the opportunity to be developed or tested under the supervision and with the involvement of expert (and other support) government for compliance with future regulation.
As part of the sandbox, products will be “sifted” for compliance with the entire range of future regulatory requirements. First of all, the products that will be processed within the sandbox will be of sufficient interest for the state, as well as those that meet other selection criteria, will be included in the sandbox. It is expected that these will be, for example, such criteria as the social significance of the product. There will also be certain selection privileges for small and medium-sized enterprises and startups.
Voluntary labeling of AI systems
Labeling AI systems is providing clear and structured information about the construction, functions, algorithms, and other aspects of AI systems. This process aims to ensure transparency and openness about exactly how intelligent systems work.
Clear labeling demonstrates that AI developers and system integrators are responsible for their products and their implementation and are transparent about system disclosures. If an AI system causes harm or behaves unexpectedly, it is important to know who is responsible for fixing the situation. This will build trust among users and avoid bias and discrimination.
The developer will go through the labeling procedure voluntarily, for example, using a web form. The webform allows the developer or system owner to “tell” the AI system in a standardized way, voluntarily providing information about three key elements—training data, algorithms, and decision space.
Center for Responsible AI
An equally important tool is the center of responsible AI in the form of a web portal. The goal is to provide convenient access to all tools, as well as to keep all key stakeholders constantly updated on how Ukraine is moving towards the introduction of mandatory regulation and how it is being implemented.
Challenges
One of the challenges on the way to the implementation of AI regulation is called by the Ministry of Digitization the need to create a regulatory body that will implement relevant legislation in the field of AI and monitor its compliance. However, the creation of such a regulatory body requires a sufficient number of human and financial resources, which, despite the importance of AI, is extremely unlikely in wartime conditions.
In addition, the creation of such a body requires time to go through all the necessary procedures, in particular, the development of a separate law on the order of creation, powers and functions of such a body. Another important problem is the availability of an appropriate level of expertise and professional human resources that can be involved in the work of the regulatory body.
“That is why we focus on capacity building within our approach, where capacity building means not only the business’s ability to meet future requirements, but also the state’s ability to regulate. And that is why, for example, an approach with the rapid implementation of mandatory regulation with the creation of a regulatory body (implementation of the EU Regulation immediately after its adoption) is actually impossible,” the White Book states.